Choices & Forks
A Fork is an element that splits the path flow into multiple parallel paths. It implicitly ends in a Join, where all
paths come together again. To reach the state after the Join, all paths need to reach the Join.
Choice
Section titled “Choice”A Choice is a conditional branching element in the state machine.
It allows the state machine to move from one point in the flow to one of multiple alternative paths based on the event value provided.
Each path inside a Choice may require one or more specific event values to be taken.
Example
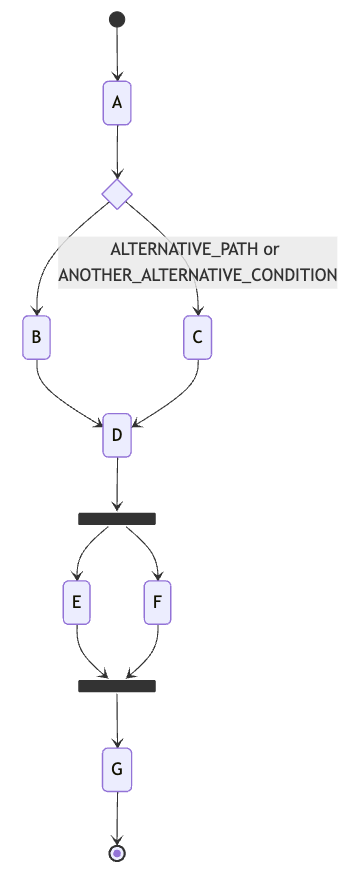
Section titled “Example”This example demonstrates the combined behavior of Choice (conditional branching) and Fork (parallel execution) inside a state machine, where specific event values direct which path is taken at a choice, and parallel branches progress independently before joining again.
from perseus.state_machine.StateMachine import StateMachine
...
choice_path_1 = Path(("B", None))choice_path_2 = Path(("C", ["ALTERNATIVE_PATH", "ANOTHER_ALTERNATIVE_CONDITION"]))choice = Choice(choice_path_1, choice_path_2)
fork_path_1 = Path(("E", None))fork_path_2 = Path(("F", None))fork = Fork(fork_path_1, fork_path_2)
top_level_path = Path(("A", None), (choice, None), ("D", None), (fork, None), ("G", None))state_machine = StateMachine(top_level_path)
state_machine.add_event(Event("A", "CLASSIC_PATH")) # current states after event: ["B"]state_machine.add_event(Event("B", None)) # current states after event: ["D"]state_machine.add_event(Event("D", None)) # current states after event: ["E", "F"]state_machine.add_event(Event("F", None)) # current states after event: ["E"]state_machine.add_event(Event("E", None)) # current states after event: ["G"]The state machine starts at state A.
It then encounters a Choice followed by D, a Fork, and finally state G.
- The Choice branches from
Ainto two possible paths:- Path 1: State
B(taken if event value does not match alternative conditions). - Path 2: State
C(taken if event value is one ofALTERNATIVE_PATHorANOTHER_ALTERNATIVE_CONDITION).
- Path 1: State
- The Fork later splits the path flow from
Dinto two parallel paths:- Path 1: State
E. - Path 2: State
F.
- Path 1: State
Graphical representation
Section titled “Graphical representation”