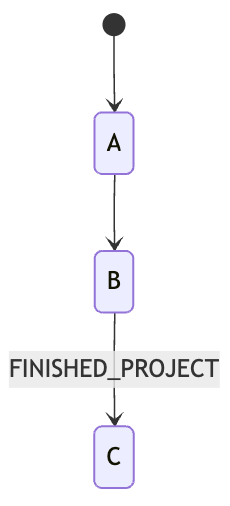
Simple state machine
from perseus.state_machine.StateMachine import StateMachine
...
simple_path = Path(("A", None), ("B", None), ("C", ["FINISHED_PROJECT"]))simple_state_machine = StateMachine(simple_path)
simple_state_machine.current_states() # will return ["A"]simple_state_machine.add_event(Event("A", None)) # state A fires event with no contentsimple_state_machine.current_states() # will return ["B"]simple_state_machine.add_event(Event("B", None)) # state B fires event with no contentsimple_state_machine.current_states() # will return ["B"] because C requires the event value "FINISHED_PROJECT"simple_state_machine.add_event( Event("B", "FINISHED_PROJECT")) # state B fires event with value "FINISHED_PROJECT"simple_state_machine.current_states() # will return ["C"]This state machine consists of a defined path made up of three states: A, B, and C.
Each step in the path can require a specific event value to trigger the transition to the next state.
In this example:
- The state machine starts at state
A. - The transition from
AtoBoccurs when an event fromAwith no value is fired. - To move from
BtoC, an event fromBwith the valueFINISHED_PROJECTmust be fired. If the event fromBhas no value, the state machine stays inB. - Once the correct event is received, the state transitions to
C.
Graphical representation
Section titled “Graphical representation”